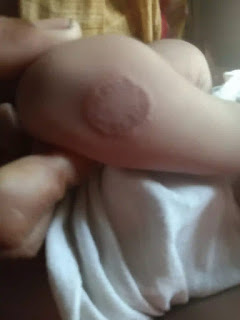
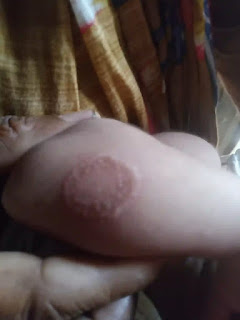
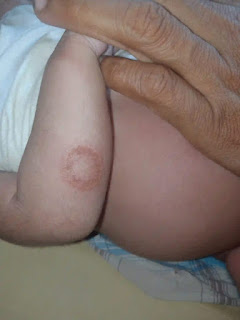
Courtesy: Dr.Harunor rasid
Tinea, commonly known as ringworm, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin, nails, and scalp. Despite its name, it is not caused by worms but by various types of fungi known as dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm and moist environments, making certain areas of the body more susceptible to infection.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Tinea can be contracted through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated objects, such as clothing, towels, or surfaces. The fungi can also be acquired from animals, especially cats and dogs, who may carry the infection on their fur.
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing tinea. These include:
Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are more susceptible to fungal infections, including tinea.
Poor Hygiene: Insufficient personal hygiene practices, such as infrequent handwashing or sharing personal items, can increase the risk of infection.
Warm and Humid Environments: Excessive sweating and prolonged exposure to warm and moist environments create an ideal breeding ground for fungi, making individuals more susceptible to tinea.
Close Contact with Infected Individuals: Participating in activities that involve close skin-to-skin contact, such as contact sports or sharing communal spaces like gyms or locker rooms, can increase the risk of contracting tinea.
Common Types and Symptoms:
Tinea can manifest in various forms, each affecting different areas of the body:
Tinea Corporis (Ringworm of the Body): This type affects the skin, presenting as red, scaly patches with well-defined borders. These patches often have a raised, ring-shaped appearance and can be itchy and inflamed.
Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot): Athlete's foot primarily affects the feet, particularly between the toes. It causes itching, burning, and cracking of the skin, often accompanied by redness and blisters.
Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch): Commonly affecting the groin area, jock itch appears as a red, itchy rash. It may spread to the inner thighs, buttocks, and genitals and can be more prevalent in males.
Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm): Scalp ringworm typically affects children and is characterized by itchy, scaly patches on the scalp. It can lead to hair loss and may present as small, bald spots.
Tinea Unguium (Nail Fungus): Nail fungus affects the nails, causing them to become thick, discoloured, brittle, and crumbly. The nails may also separate from the nail bed.
Treatment and Prevention:
Prompt and appropriate treatment is essential to manage tinea effectively. Over-the-counter antifungal creams, sprays, or powders can be used for mild cases of tinea corporis, pedis, and cruris. However, more severe or persistent infections may require prescription antifungal medications, either in topical or oral form.
To prevent tinea and reduce the risk of recurrence, the following measures are recommended:
Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly wash and dry the affected areas, ensuring they are clean and dry throughout the day. Avoid sharing personal items like towels, clothing, or shoes.
Keep Skin Dry: Moisture creates an environment conducive to fungal growth, so ensure that skin folds, such as those in the groin area, are kept dry.
Wear Appropriate Footwear: Choose breathable shoes and moisture-wicking socks to prevent excessive sweating and maintain proper foot hygiene.
Practice Proper Nail Care: Keep nails clean and trimmed and avoid sharing nail clippers or other manicure tools. If you suspect a nail fungus infection, seek prompt treatment to prevent its spread to other nails.
5. Protect Feet in Public Areas: When using public showers, pools, or locker rooms, wear sandals or flip-flops to minimize direct contact with potentially contaminated surfaces.
Treat Infected Pets: If you have a pet with a fungal infection, seek veterinary care and follow the recommended treatment to prevent transmission to humans.
Boost Immune System: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management, to support a strong immune system that can help fight off infections.
While tinea infections are generally not serious, prompt treatment is crucial to prevent their spread and alleviate symptoms. If you suspect you have tinea or have persistent or severe symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Remember, proper hygiene practices and proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of tinea infections. By staying informed and adopting preventive measures, you can minimize the chances of contracting tinea and maintain healthy skin, nails, and scalp.